KSelectionProxyModel Class
A Proxy Model which presents a subset of its source model to observers. More...
| Header: | #include <KSelectionProxyModel> |
| CMake: | find_package(KF6 REQUIRED COMPONENTS ItemModels)target_link_libraries(mytarget PRIVATE KF6::ItemModels) |
| Inherits: | QAbstractProxyModel |
Properties
- filterBehavior : FilterBehavior
- selectionModel : QItemSelectionModel*
Public Functions
| KSelectionProxyModel() | |
| KSelectionProxyModel(QItemSelectionModel *selectionModel, QObject *parent = nullptr) | |
| KSelectionProxyModel::FilterBehavior | filterBehavior() const |
| QItemSelectionModel * | selectionModel() const |
| void | setFilterBehavior(KSelectionProxyModel::FilterBehavior behavior) |
| void | setSelectionModel(QItemSelectionModel *selectionModel) |
Signals
| void | filterBehaviorChanged() |
| void | selectionModelChanged() |
Detailed Description
The KSelectionProxyModel is most useful as a convenience for displaying the selection in one view in another view. The selectionModel of the initial view is used to create a proxied model which is filtered based on the configuration of this class.
For example, when a user clicks a mail folder in one view in an email application, the contained emails should be displayed in another view.
This takes away the need for the developer to handle the selection between the views, including all the mapToSource(), mapFromSource() and setRootIndex() calls.
MyModel *sourceModel = new MyModel(this); QTreeView *leftView = new QTreeView(this); leftView->setModel(sourceModel); KSelectionProxyModel *selectionProxy = new KSelectionProxyModel(leftView->selectionModel(), this); selectionProxy->setSourceModel(sourceModel); QTreeView *rightView = new QTreeView(this); rightView->setModel(selectionProxy);
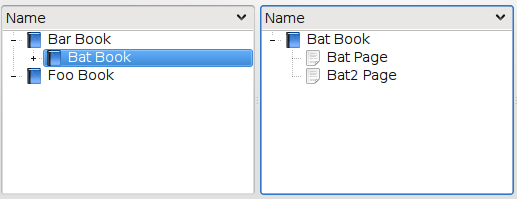
The KSelectionProxyModel can handle complex selections.
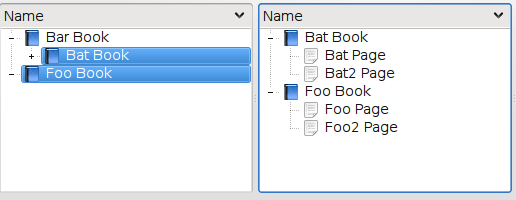
The contents of the secondary view depends on the selection in the primary view, and the configuration of the proxy model. See KSelectionProxyModel::setFilterBehavior for the different possible configurations.
For example, if the filterBehavior is SubTrees, selecting another item in an already selected subtree has no effect.
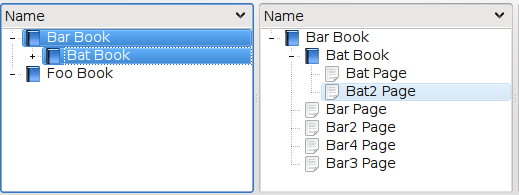
See the test application in tests/proxymodeltestapp to try out the valid configurations.
Obviously, the KSelectionProxyModel may be used in a view, or further processed with other proxy models. See KAddressBook and AkonadiConsole in kdepim for examples which use a further KDescendantsProxyModel and QSortFilterProxyModel on top of a KSelectionProxyModel.
Additionally, this class can be used to programmatically choose some items from the source model to display in the view. For example, this is how the Favourite Folder View in KMail works, and is also used in unit testing.
See also: Proxy Models in the Qt Documentation
Property Documentation
filterBehavior : FilterBehavior
Access functions:
| KSelectionProxyModel::FilterBehavior | filterBehavior() const |
| void | setFilterBehavior(KSelectionProxyModel::FilterBehavior behavior) |
Notifier signal:
| void | filterBehaviorChanged() | [see note below] |
Note: This is a private signal. It can be used in signal connections but cannot be emitted by the user.
selectionModel : QItemSelectionModel*
Access functions:
| QItemSelectionModel * | selectionModel() const |
| void | setSelectionModel(QItemSelectionModel *selectionModel) |
Notifier signal:
| void | selectionModelChanged() | [see note below] |
Note: This is a private signal. It can be used in signal connections but cannot be emitted by the user.
Member Function Documentation
[explicit] KSelectionProxyModel::KSelectionProxyModel()
Default constructor. Allow the creation of a KSelectionProxyModel in QML code. QML will assign a parent after construction.
[explicit] KSelectionProxyModel::KSelectionProxyModel(QItemSelectionModel *selectionModel, QObject *parent = nullptr)
Constructor.
selectionModel The selection model used to filter what is presented by the proxy.
void KSelectionProxyModel::setFilterBehavior(KSelectionProxyModel::FilterBehavior behavior)
Set the filter behaviors of this model. The filter behaviors of the model govern the content of the model based on the selection of the contained QItemSelectionModel.
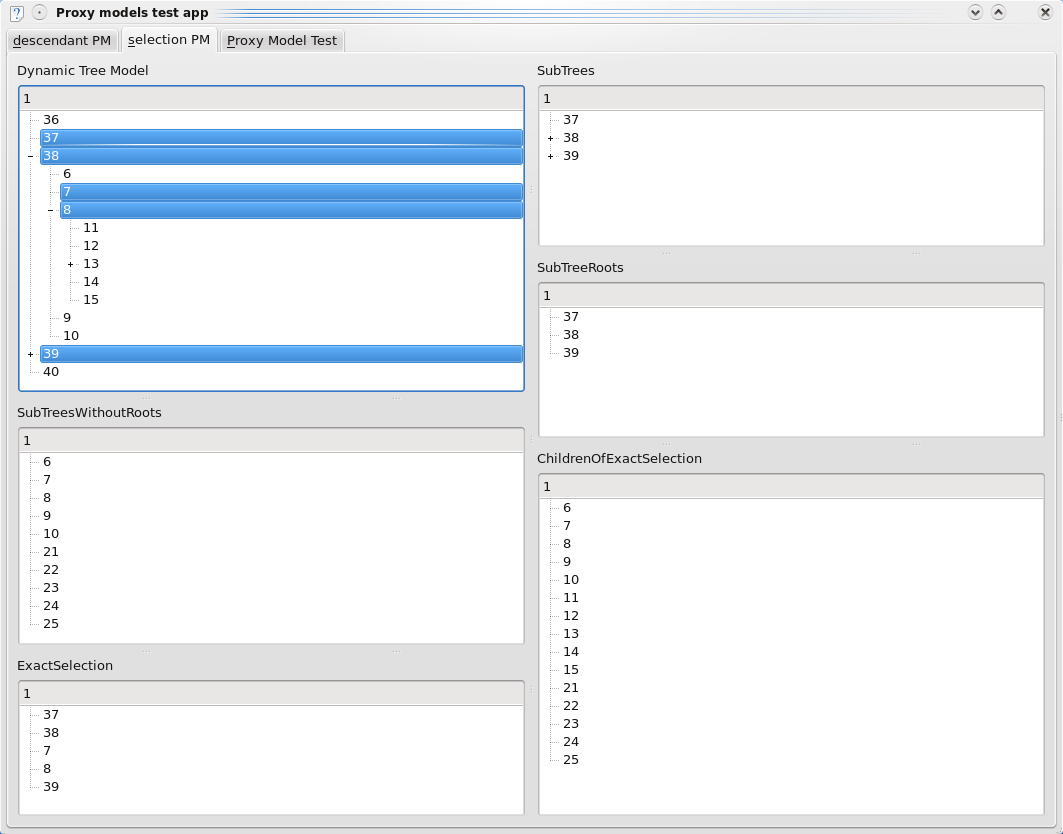
See kdeui/proxymodeltestapp to try out the different proxy model behaviors.
The most useful behaviors are SubTrees, ExactSelection and ChildrenOfExactSelection.
The default behavior is SubTrees. This means that this proxy model will contain the roots of the items in the source model. Any descendants which are also selected have no additional effect. For example if the source model is like:
(root) - A - B - C - D - E - F - G - H - I - J - K - L
And A, B, C and D are selected, the proxy will contain:
(root) - A - B - C - D - E - F - G
That is, selecting 'D' or 'C' if 'B' is also selected has no effect. If 'B' is de-selected, then 'C' amd 'D' become top-level items:
(root) - A - C - D - E - F - G
This is the behavior used by KJots when rendering books.
If the behavior is set to SubTreeRoots, then the children of selected indexes are not part of the model. If 'A', 'B' and 'D' are selected,
(root) - A - B
Note that although 'D' is selected, it is not part of the proxy model, because its parent 'B' is already selected.
SubTreesWithoutRoots has the effect of not making the selected items part of the model, but making their children part of the model instead. If 'A', 'B' and 'I' are selected:
(root) - C - D - E - F - G - J - K - L
Note that 'A' has no children, so selecting it has no outward effect on the model.
ChildrenOfExactSelection causes the proxy model to contain the children of the selected indexes,but further descendants are omitted. Additionally, if descendants of an already selected index are selected, their children are part of the proxy model. For example, if 'A', 'B', 'D' and 'I' are selected:
(root) - C - D - E - G - J - K - L
This would be useful for example if showing containers (for example maildirs) in one view and their items in another. Sub-maildirs would still appear in the proxy, but could be filtered out using a QSortfilterProxyModel.
The ExactSelection behavior causes the selected items to be part of the proxy model, even if their ancestors are already selected, but children of selected items are not included.
Again, if 'A', 'B', 'D' and 'I' are selected:
(root) - A - B - D - I
This is the behavior used by the Favourite Folder View in KMail.
Note: Setter function for property filterBehavior.
See also filterBehavior().